# Reference
# Init factory
2D Engine is created using a factory you get as default export from the package:
import makeViewer from "@bimdata/2d-engine"; // webpack / rollup
const canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
const viewer = makeViewer({ canvas });
2
3
4
canvas is mandatory and another properties can be passed to customized the 2D Engine behavior:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
canvas | HTMLCanvasElement | Required. |
autoStart | boolean | Default = true. If false, you must call viewer.ticker.start() to start rendering. |
select | boolean | Default = true. If false, disabled the select layer. |
highlight | boolean | Default = true. If false, disabled the highlight layer. |
picking | boolean | Default = true. If false, disabled the picking layer. |
snap | boolean | Default = true. If false, disabled the snap layer. |
The factory returns the viewer with the following interface:
interface Viewer {
readonly canvas: HTMLCanvasElement;
readonly scene: Scene;
readonly camera: Camera;
destroy(): void;
readonly renderer: Renderer;
readonly textureManager: TextureManager;
readonly styles: { default: Style; selected: Style; highlight: Style };
readonly settings: Settings;
readonly constants: Constants;
readonly picker: Picker;
readonly snapper: Snapper;
readonly ticker: Ticker;
readonly ui: UI;
readonly utils: {
readonly vector2D: Vector2DUtils;
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Scene
The viewer scene is where model and objects lives. You can add/remove models and objects and getters and setters allow read/write objects in batch.
It has the following interface:
interface Scene extends Readonly<EventHandler> {
readonly viewer: Viewer;
// Models
readonly models: Model[];
readonly modelsMap: Map<number, Model>;
addModel(modelData: ModelData): Model;
removeModel(id: number): boolean;
// Objects
readonly objects: SceneObject[];
readonly objectsMap: Map<number, SceneObject>;
addObject(objectData: SceneObjectData, model?: Model): SceneObject;
removeObject(objectId: number): boolean;
// Objects setters
showObjects(ids: number[]): void;
hideObjects(ids: number[]): void;
selectObjects(ids: number[]): void;
deselectObjects(ids: number[]): void;
highlightObjects(ids: number[]): void;
unhighlightObjects(ids: number[]): void;
setObjectsPickable(ids: number[]): void;
setObjectsUnpickable(ids: number[]): void;
// Object getters
readonly shownObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly hiddenObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly selectedObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly unselectedObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly highlightedObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly unhighlightedObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly pickableObjects: SceneObject[];
readonly unpickableObjects: SceneObject[];
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# Events
The following events are emitted by the 2D Engine scene :
- "model-added", payload: the added model.
- "model-removed", payload: the removed model.
- "object-added", payload: the added object.
- "object-removed", payload: the removed object.
- "object-update", payload: { object, property, value?, oldValue? }. No value and oldValue for the "geometry" property.
Events can be listened using scene.on:
viewer.scene.on("model-added", (model) =>
console.log(`A model is loaded with the id ${model.id}`)
);
2
3
# Styles
Styles define how objects are drawn by default when they are visible, selected and highlighted. It can be customized by changing the default styles (WARNING: updating styles.default won't affect already loaded objects) or loading objects with non default style.
A style has the following interface:
interface Style {
// TEXTURE
texture?: string;
textureTint?: number;
textureOpacity?: number;
// LINE
lineWidth?: number;
lineColor?: number;
lineOpacity?: number;
lineDash?: number[];
lineCap?: LINE_CAP;
lineJoin?: LINE_JOIN;
}
enum LINE_CAP {
BUTT,
ROUND,
SQUARE,
}
enum LINE_JOIN {
BEVEL,
MITER,
ROUND,
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
You can change textureTint and lineColor using hexadecimal numbers.
viewer.scene.styles.default.textureTint = 0xff0000; // For red. (RGB)
textureOpacity and lineOpacity are numbers between 0 and 1.
lineDash is an array of numbers describing the dash pattern you want to use. See hereopen in new window for more informations.
# Texture Manager
The Texture Manager has the following interface:
interface TextureManager {
textureMatrix: TextureMatrix;
load(
name: string,
src: string,
width?: number,
height?: number
): Nullable<Object>;
}
// and the interface of the texture matrix
interface TextureMatrix {
rotate(angle: number): void;
scale(x: number, y?: number): void;
translate(x: number, y: number): void;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
The viewer only have "solid" texture built in but it is possible to load more:
await viewer.scene.textureManager.load(
"myTextureName",
"./my/textures/folder/myTexture.png"
);
2
3
4
NOTE: this is async code and must be awaited in order to the texture to ba available in the viewer.
This is what you can get: (wall are textured using a cross hatch texture)
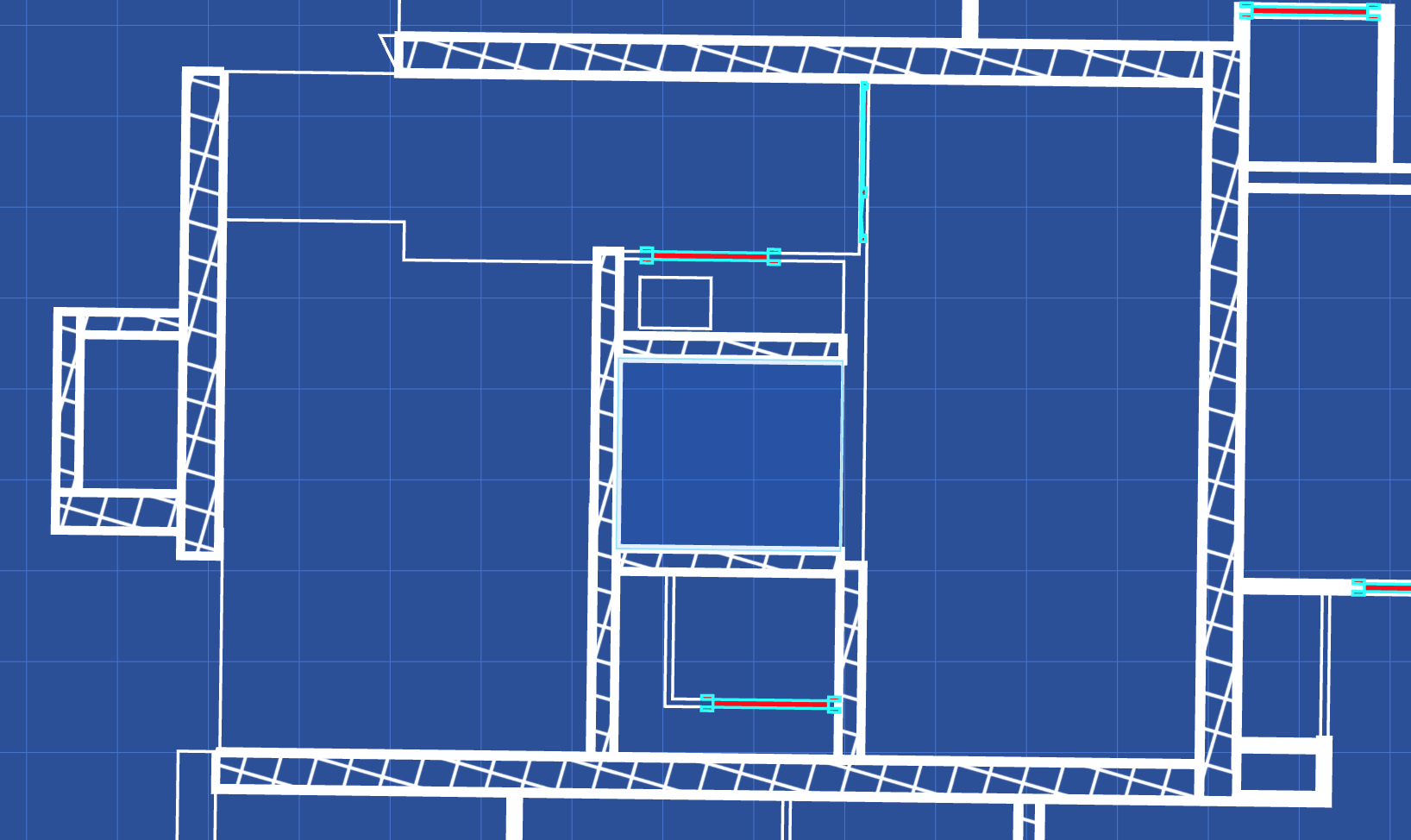
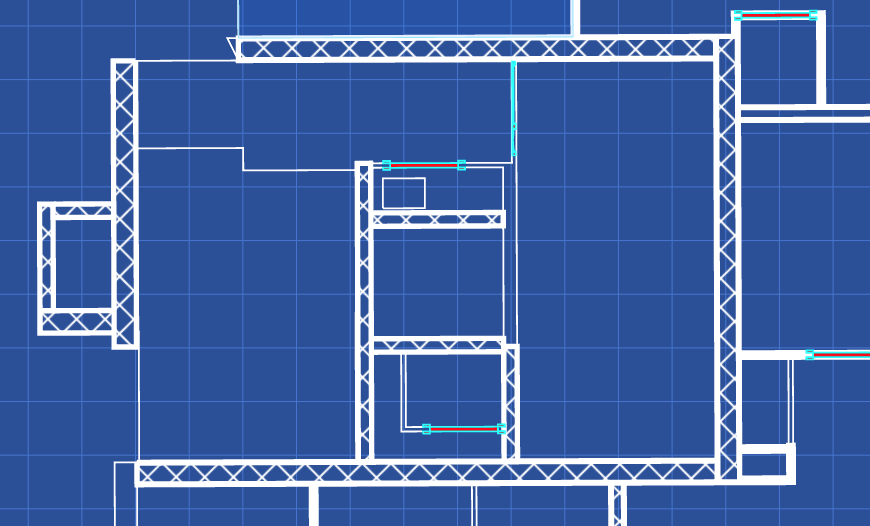
Notice that the textrure is aligned with the axis. If the model is not aligned with the axis, you can use the Texture Manager textureMatrix to rotate the textures.
viewer.scene.textureManager.textureMatrix.rotate(30);
# Model and Objects
# Model
To add a model to the scene, use the scene.addModel(modelData: ModelData) method.
interface ModelData {
readonly id?: string;
readonly objects?: SceneObjectData[];
}
interface Model extends Positionable, Transformable {
readonly id: number;
readonly scene: Scene;
readonly objects: SceneObject[];
addObject(objectData: SceneObjectData): SceneObject;
removeObject(objectId: number): boolean;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Object
To add object to the scene, you can use the scene.addObject(objectData: ObjectData) or the model.addObject(objectData: ObjectData) methods, or add it through models.
interface SceneObjectData extends Style {
visible: boolean;
selected: boolean;
highlighted: boolean;
pickable: boolean;
readonly id?: string;
readonly zIndex?: number;
readonly pickingZIndex?: number;
readonly geometry?: GeometryData;
}
interface SceneObject extends Style, Positionable, Transformable {
readonly id: number;
readonly scene: Scene;
readonly model: Model;
readonly geometry: Geometry;
// Scene state properties
visible: boolean;
selected: boolean;
highlighted: boolean;
pickable: boolean;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Objects extends the Style interface. Each object style properties can be updated on the fly leading to a new render.
object.lineWidth = 4;
# Geometry
Objects have geometry and a geometry is an array of shape.
type GeometryData = Array<number[] | LineData | ArcData | CurveData>;
interface ShapeData {
type?: ShapeType;
closePath: boolean; // If true, the path is closed after this shape and another path is opened for the following shapes. Equivalent of the svg command "Z".
startPath: boolean; // If true, a new path is started before drawing this shape.Equivalent of the svg command "M".
}
interface Geometry extends Positionable {
readonly shapes: Shape[];
getShape(index?: number): Shape | undefined;
addShape(shape: ShapeData | PointsData, index?: number): Shape;
removeShape(index?: number): Shape | undefined;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Path API
By default, each shapes are drawn like a single path (linked together without stoping the drawing line). But this behaviour can be changed using the startPath and closePath booleans. The default value for startPath is false except for the first shape and the shapes that followed a shape with closePath at true. The default value for closePath is false.
Here is an example of these APIs.
const object = {
geometry: [
{
type: "line",
points: [300, 0, 350, 50, 400, 0],
startPath: true,
},
{
type: "line",
points: [300, 50, 350, 100, 400, 50],
startPath: true,
},
{
type: "line",
points: [300, 100, 350, 150, 400, 100],
startPath: true,
},
{
type: "arc",
x: 350,
y: 250,
radius: 50,
startPath: true,
closePath: true,
},
],
texture: "solid",
textureTint: 0xff0000,
textureOpacity: 0.5,
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
This object is drawn like this:
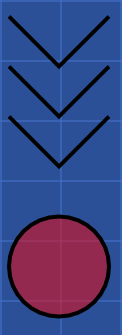
If the startPath propertiy is removed:
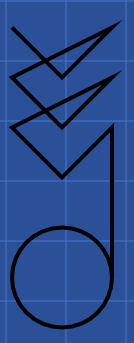
In this example, the closePath property helps the drawing engine to correctly close the cirle.
# Add geometry
When adding objects on a scene, shapes can be provide to object using the geometry property. By default, array of numbers will be displayed as lines.
const model = viewer.scene.addModel({
objects: [
{
geometry: [
[0, 0, 50, 50], // a line
{
type: "line", // another line
points: [0, 50, 50, 0],
// poly: true // if poly = true, the shape is closed between the last point and the first.
},
{
type: "arc", // a default arc => full circle
x: 25,
y: 25,
radius: 20,
},
],
},
],
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
TIP
Geometries can be edited on the fly. To see how, try it hereopen in new window.
The viewer handle three shape types: line, arc and curve.
# Line
interface LineData extends ShapeData {
type: ShapeType.line;
points: PointsData;
poly?: boolean;
}
interface Line {
readonly type: ShapeType.line;
readonly points: Point[];
getPoint(index?: number): Point | undefined;
addPoint(point: Point, index?: number): Point;
removePoint(index?: number): Point | undefined;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Arc
interface ArcData extends ShapeData {
type: ShapeType.arc;
x: number;
y: number;
radius: number;
startAngle?: number; // (0 is at the 3 o'clock position of the arc's circle)
endAngle?: number;
anticlockwise?: boolean;
composite?: boolean; // default to `false`, `true` to be linked with the previous shape.
}
interface Arc {
readonly type: ShapeType.arc;
x: number;
y: number;
radius: number;
startAngle: number; // Degrees from the right of the arc.
endAngle: number; // Degrees from the right of the arc.
anticlockwise?: boolean;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# Curve
interface CurveData extends ShapeData {
type: ShapeType.curve;
x: number;
y: number;
cpX1: number;
cpY1: number;
cpX2: number;
cpY2: number;
toX: number;
toY: number;
}
interface Curve extends Shape {
readonly type: ShapeType.curve;
x: number;
y: number;
cpX1: number;
cpY1: number;
cpX2: number;
cpY2: number;
toX: number;
toY: number;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Positionable & Transformable
These APIs allows to get and update the position of the corresponding entity:
type AABB = [minX: number, minY: number, maxX: number, maxY: number];
interface Point {
x: number;
y: number;
}
interface Positionable {
aabb: AABB;
center: Point;
}
interface Transformable {
move(position: Point): void;
translate(dx: number, dy: number): void;
/**
* @param angle in degree, clockwise
* @param origin
*/
rotate(angle: number, origin?: Point): void;
scale(ds: number, origin?: Point): void;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# UI
The UI is the only component connected to a DOM element, listening to events. It has the following interface:
interface UI extends EventHandler<UIHandlerEvents> {
connect(el: HTMLElement): void;
disconnect(): boolean;
}
2
3
4
The camera and the picker listen to the UI events. Disconnecting the UI will make them not reactive to user interactions.
# Events
- "click", payload: { canvasPosition, keys }
- "right-click", payload: { canvasPosition, keys }
- "move", payload: { canvasPosition, keys }
- "drag", payload: { dx, dy, keys }
- "scroll", payload: { canvasPosition, dx, dy, keys }
- "exit", no payload, when the mouse leave
el.
# Camera
The camera is binded on the mouse events. It has the following interface:
/**
* A camera allows to see the world. Two coordinate systems can be manipulated using it:
* - the world coordinates, mentionned as `position`.
* - the canvas coordinates, mentionned as `canvasPosition`.
*
* A camera emits events:
* - "update", payload { MatrixExtended } : the camera transform. Emited when the camera is updated.
*
* To express the zoom level, the camera has two units:
* - zoom, expressed in percentages, as 100 times the scale.
* - scale ]0,+Infitiy[.
*
*/
interface Camera
extends Transformable,
Readonly<EventHandler<{ update: PIXITransform }>> {
fitView(
target: Scene | Scene[] | Model | Model[] | SceneObject | SceneObject[]
): void;
destroy(): void;
controller: CameraController;
/**
* @param factor ]-Infinity, +Infinity[
* @param origin the zoom transform center.
*/
zoomIn(factor?: number, origin?: Point): void;
/**
* @param factor ]-Infinity, +Infinity[
* @param origin the zoom transform center.
*/
zoomOut(factor?: number, origin?: Point): void;
/**
* @param angle in degree clockwise.
* @param origin the rotation transform center.
*/
transform: PIXIMatrix;
position: Point;
/**
* @returns { number } the camera rotation angle in degree clockwise.
*/
rotation: number;
/**
* @returns { number } ]-Infinity, +Infinity[
*/
getScale(): number;
/**
* @returns { number } ]0, +Infinity[
*/
zoom: number;
/**
* Returns the position of the given canvas position.
*/
getPosition(canvasPosition: Point): Point;
/**
* Returns the canvas position of the given position.
*/
getCanvasPosition(position: Point): Point;
getViewpoint(): Viewpoint;
setViewpoint(viewpoint: Viewpoint): Viewpoint;
}
interface Viewpoint {
x: number;
y: number;
/**
* degree clockwise
*/
rotation: number;
/**
* ]-Infinity, +Infinity[
*/
zoom: number;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
It is possible to customise the camera behaviour by changing the properties of the camera.controller that has the following interface:
interface CameraController {
translatable: boolean;
rotatable: boolean;
scallable: boolean;
}
2
3
4
5
All properties are true by default.
# Picker
The picker allows to get objects under the mouse pointer.
interface Picker extends Readonly<EventHandler> {
pick(x: number, y: number): SceneObject | undefined;
}
2
3
You may be mainly interseted by the picker events:
- "pick", payload : { object, position, keys, rightClick: boolean }
- "pick-nothing", payload: { position, keys, rightClick: boolean }
- "hover-surface", payload: { object, position }
- "hover", payload: { object, position }
- "hover-out", payload: { object, position }
- "hover-off", payload: { position }
viewer.camera.controller.on("pick", ({ object }) => {
object.selected = !object.selected;
});
2
3
# Snapper
The snapper allows to get a line vertex or edge position close to the given canvas position:
interface Snapper {
getSnap(canvasPosition: Point, options?: SnapOptions): Point;
}
interface SnapOptions {
canvasDistance?: number; // default 20
snapVertices?: boolean; // default true
snapLines?: boolean; // default true
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Example to move a object close to another with the snap:
const object = viewer.scene.addObject({ /* scene object data */});
viewer.ui.on("move", ({ canvasPosition }) => {
const point = viewer.snapper.getSnap(canvasPosition);
object.move(point ?? viewer.camera.getPosition(canvasPosition));
});
);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Settings
Settings are predefined values/keys that define the 2D Engine behaviour. It has the following interface:
interface Settings {
rotateKey: string; // default "shift"
scaleSpeed: number; // default 0.002
rotateSpeed: number; // default 0.1
maxScale: number; // default 1000
minScale: number; // default 0.001
fitViewRatio: number; // default 0.9
snapMargin: number; // default 1
curves: {
adaptive: boolean;
maxLength: number;
maxSegments: number;
minSegments: number;
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Ticker
Use viewer.ticker.start/stop() to start or stop the rendering.
Use viewer.ticker.add/addOnce(name: string, callBack: Function) to schedule a callback on the next tick. The callback will be called with dt, the delta time since the next tick. WARNING: adding many tasks with the same name will overide the previous tasks and only the last added will be called on the next tick. This can be used to do not overdue a callback that must be done only once per tick.
# Renderer
Renderer emits events you can use for addons:
- "resize", payload: { dx: number, dy: number }. Emited when the renderer resizes.
- "pre-draw". Emited before the draw phase.
- "post-draw". Emited after the draw phase.
# Vector2DUtils
It exposes some methods to work with 2D vectors:
interface Vector2DUtils {
distance(v1: Vector2D, v2: Vector2D): number;
sub(v1: Vector2D, v2: Vector2D): Vector2D;
add(v1: Vector2D, v2: Vector2D): Vector2D;
normalize(v: Vector2D): Vector2D;
length(v: Vector2D): number;
dot(v1: Vector2D, v2: Vector2D): number;
cross(v1: Vector2D, v2: Vector2D): number;
rotateAround(v: Vector2D, center: Vector2D, angle: number): Vector2D;
angle(v1: Vector2D, v2: Vector2D): number;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
WARNING
Angles are expressed in radians in Vector2DUtils.
